As we have written about in the past the Qt framework is applicable for a wide range of software projects. To be honest, almost for all sorts of projects, yeah :). One more commercial segment where this framework is currently being applied widely in the automotive sector. Now many models are equipped with instrument clusters and in-vehicle infotainment systems written using the Qt platform and it is no mere chance!
At the June, 2016 the Qt Company announced the launch of the Qt Automotive Suite. However, today the software market suggests other similar tools like Dash or Kanzi. But we feel that Qt is the perhaps most promising tool. Currently, it is quite possible that the Qt framework has already been applied by such giants as BMW Group, Honda, Volvo, and other manufacturers. We suspect this to be true although there is no open data available confirming it.
- Genivi
- Branches
- In-Vehicle Infotainment (IVI) Systems
- Instrument Clusters
- Head-Up Display (HUD)
- Connected Car Environment
- Navigation and Info Systems
- Anatomy of Qt Automotive Suite
- Qt IVI Module
- Qt Device Creation
- Application Manager and Compositor
- Boot to Qt
- Qt Fast Boot Instrument Cluster
- Qt 3D Studio
- Qt Safe Renderer
- Multiple Display with a Single Processor
- Mapbox
- QNX Hypervisor
Genivi
Before we continue to talk about the role of Qt in the automotive industry it is necessary to note the parent organization that suggests certain standards for the automotive development process. It is the Genivi Alliance. Genivi is an open development community of automotive software components that includes more than 120 companies. The participants have agreed upon standard APIs, and a development platform for in-vehicle infotainment (IVI) and other connected vehicle solutions. The Genivi Alliance provides methods of producing automotive software. Mostly these are open source projects (like Linux OS). Genivi has its own development platform (GDP) that connects both automotive and non-automotive developers to be able to prototype new solutions in the automotive sector. GDP is meant to be used both on professional automotive hardware platforms (Intel, Renesas, nVidia, Qualcomm) and on low-cost boards like the Raspberry Pi 2/3. Genivi original equipment manufacturers are: BMW Group, Honda, Hyundai Motor Group, Jaguar / Land Rover, Daimler, Nissan, PSA Group, Renault and Volvo. Also, the alliance consists of numerous other companies that produce spare parts,
hardware components, software solutions and services for the automotive industry.
Branches
The Qt framework is applied most often for the following branches in the automotive industry:
In-Vehicle Infotainment (IVI) Systems
Qt applications for IVI allows the implementation of systems with multiple screens. Such IVI are multi-process and multi-app architecture and can be easily integrated with 3rd party software.

Instrument Clusters
It is possible to build digital instrument clusters with both 2D and 3D UIs. Such clusters have a unified User Experience (UX) across all screens. Multiple screens on a single SoC without the need for a hypervisor.

Head-Up Display (HUD)
One more amazing and useful technology that presents data without requiring users to look away from their usual viewpoints are the HUD.
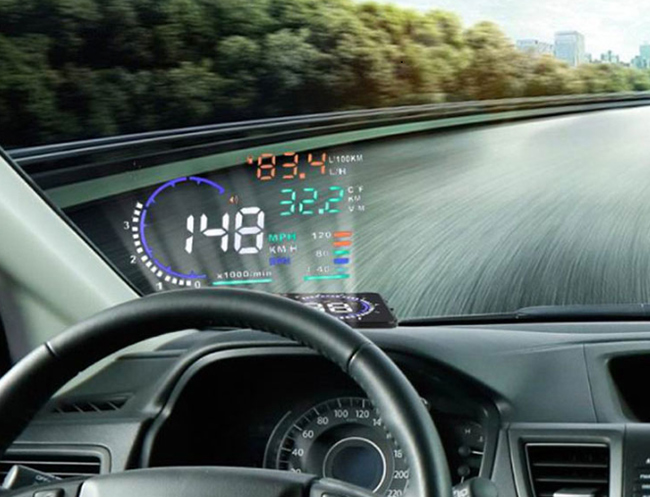

Connected Car Environment
Qt is used for the creation of automotive computer platforms. Such solutions can also include HUD and clusters and typically are a single computer that supports multiple displays, including the central unit, cluster, and HUD for a wide range of automotive customers.

Navigation and Info Systems
Navigation and information systems have been around a long time now as a high-end option in vehicles. Lately, they have been becoming a standard feature in most new vehicles.
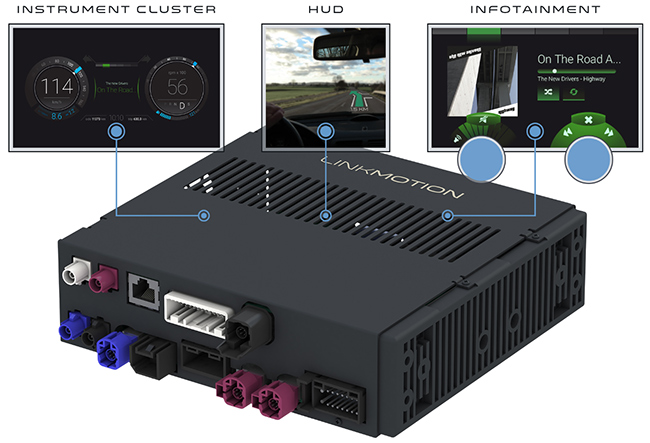
Anatomy of Qt Automotive Suite
The Qt Automotive Suite is developed for the building of IVIs faster with a combination of software components, automotive APIs and tooling. Qt Automotive Suite is a collection of software components and tools that are built on top of the Qt for Device Creation package. Qt Automotive Suite is adapted for creating full-featured IVI solutions. Also, the suite includes a reference UI for embedded platforms, reference IVI applications and application store implementations.
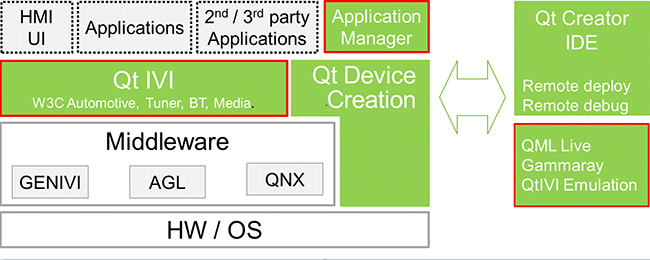
Qt IVI Module
The Qt IVI module is the core of Qt Automotive suite. It provides C++ and Qt Modeling Language (QML) interfaces for accessing vehicle features. The module includes Qt GENIVI Extras package that uses defined interfaces from the GENIVI alliance. The Qt IVI module contains helper functions to interact with the Diagnostic Log and Trace (DLT) daemon. The goal of the IVI Module is to promote reuse of the existing functionality in further versions. The Qt IVI APIs follow a pattern to provide extendable Qt interfaces integrating to the various platform middleware components used by the various OEMs.
Qt Device Creation
This module includes the QML language for building modern user interfaces, Wayland support with the Qt Wayland Compositor, Qt WebEngine based on Chromium, remote deploy and debugging directly to a target board and a comprehensive class library including multimedia and networking.
Application Manager and Compositor
The Application Manager and Compositor provide a multi-process architecture to Linux in the car. UI is split into smaller applications. These are some of such applications:
- Qt Virtual Keyboard – a complete virtual keyboard solution with word-prediction and support for multiple languages.
- Qt Quick Controls 2 – provides a set of controls for building complete user interfaces in Qt Quick.
- Qt Quick Compiler – enables the compiling of .qml source files into application binaries which improves load times and
security for code assets. - Qt WebEngine – provides a web browser engine based on the Chromium project.
Qt Automotive Suite also includes Neptune, a reference Human Machine Interface (HMI) designed for IVI systems, including multiple IVI applications and an application store implementation. It enables the OEMs to test their applications on supported hardware and emulator targets.
Boot to Qt
The automotive industry requires an almost instant boot-up time. When the car is started, the instrument cluster needs to be up, running and reacting almost immediately. At the same time, the clusters remain more digitalized and more complex. All these require extra attention to both the software design and the underlying platform/framework.
Boot to Qt is a light-weight component based on embedded Linux systems that is installed into the actual target device. This is done by flashing the device’s memory card or internal memory directly with a pre-built image that comes with the online installer.
Qt Fast Boot Instrument Cluster
To provide a fast boot up with Qt is not a problem. Just apply power to the low end hardware, 1.2 seconds later Linux has booted up and the Qt application is running.
Qt 3D Studio
Qt 3D Studio (formerly NVIDIA DRIVE Design Studio) is a tool targeted for designers to create interactive 3D interfaces and applications. Qt 3D Studio contains an in-built material and effects library and it supports the import of design assets from popular authoring tools such as Photoshop, Autodesk Maya and The Foundry MODO. With Qt 3D Studio it is easily do prototyping and product development with 3D keyframe animations and Qt Quick User Interfaces.
Qt Safe Renderer
Qt Safe Renderer tool streamlines the creation of rich graphical user interfaces for safety-critical systems. The tool enables Qt to be used in ISO 26262 ASIL-B safety-certified systems.
Multiple Display with a Single Processor
Qt Wayland and the Qt Compositor make it easy to write multi-screen applications from a single SoC.
Mapbox
Qt Automotive Suite featuring the Mapbox Vector Maps integration into Qt.
QNX Hypervisor
Instrument cluster and infotainment built with Qt.