
Bluetooth Low Energy technology is 3.5 times more popular than other technologies such as WiFi or NFC for indoor tracking . A beacon is a tool that makes such tracking possible. Now let’s take a closer look at this device. How does a beacon work? How do I deploy my own tracking system? And what are the limitations of beacons?
What is a BLE beacon?
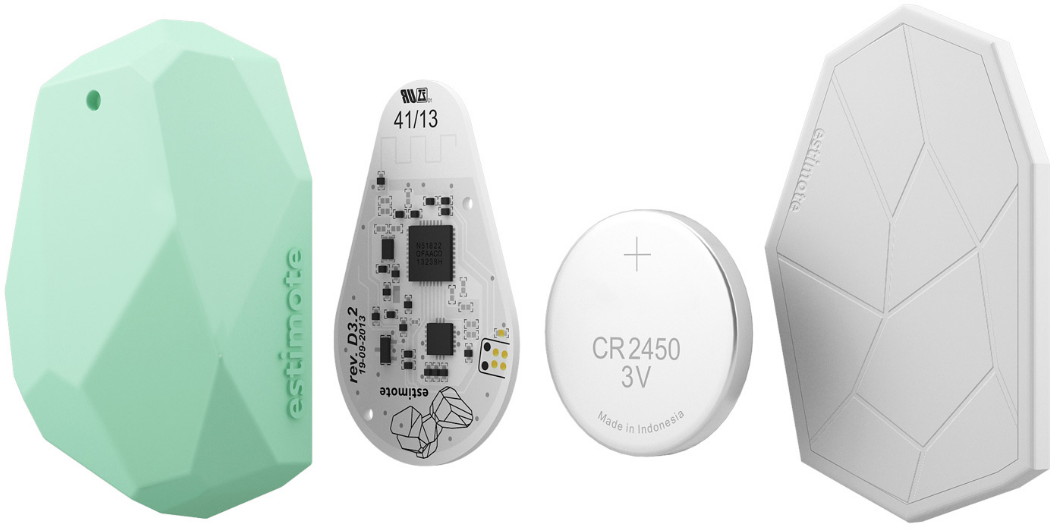
BLE Beacon is an electronic device on average 30×10 mm and 7 g with a single task: to broadcast short-range signals with different intervals (0.1 – 2 seconds) and different transmit power levels (-30 dBm – +4 dBm). A beacon consists of a small circuit board, a coin battery and a cover. The circuit board contains electronic components that are typical for a BLE chip like internal processor, antenna, and flash memory. The chipsets that are used the most often as the heart of a Beacon are Texas Instruments’ TI CC254x and Nordic Semiconductor’s nRF51822. As in a usual Bluetooth module, a beacon has a Bluetooth stack protocol, profiles and is equipped with firmware. Every beacon has its own Unique ID.
Once the beacon’s signal is caught by a nearby device (like smartphone, tablet or other electronic device) the software can display various content. It could be explanation about some nearby entity (goods, event or picture), defining location coordinates or even a suggestion to pay for the bus with CC.

BLE Beacons Usage Cases
Indoor tracking is useful for various industries. Here are some of them:
- Logistics and Manufacturing. Micro-location, indoor positioning, dispatch tracking.
- Retail. Interactive suggestions, advertisings, special offers.
- Banking. Use of beacon infrastructures to detect the presence of customers close to the bank.
- Smart Public Transportation. Dynamic or metered pricing, individual route calculation and optimization, traffic monitoring, sales, proximity marketing or advertising.
- Events. Offering visitors an interactive experience, social connections.
- Smart Cities. Avoiding bureaucracy, emergency routing, in-building navigation.
- Healthcare. Micro-location and contextual communication in hospitals.
- Building & Facility Management. Micro-location and proximity in big buildings with multiple complex destinations.
How Does Beacon Tracking Work
Map the Building. The first step in setting a tracking system based on beacons is to create a map of the building or room. Basically, this operation can be accomplished in two different ways:
1) By walking around the perimeter of each room with a smartphone with specific mapping software installed.
2) By using a tool for drawing 2D plans of a building (like ArcGIS or Google SketchUp). Then, upload the map (actually, a simple image in .png or any other format) to a dashboard.
Beacons Tuning
Beacons must be properly configured. For a minimum configuration you need to set the frame type, broadcast intervals and power levels. You will need to set an appropriate Tx power keeping in mind that it will affect lifetime of the battery. It is possible to set a beacon transmitting power anywhere from 2 m up to 70 m. With shorter broadcasting distance battery will last longer. The battery in a beacon powered up to 70 m may last only 6 months. If you cut the distance to a minimal 2 m, the same BLE tracking system might work 2 whole years without any supporting operations.
It is important to configure the beacon advertising interval. For most beacons the advertising interval is around 600 or 700 ms. This means less battery draining for the beacon than an interval 100 ms for example. Depending on the requirements of your project the advertising interval could be prolonged even more.
Once beacons have been tuned, there are different approaches to be considered for further work with beacons. One approach is to use the software that was provided by a beacon manufacturer. Each manufacturer usually has it’s own management platform. Other approach when you choose low-cost beacons is to use the official documentation. And the third approach is to use a third-party platform, which provide rich features to manage and start marketing with beacons. Some examples are: BeaconControl.io, Proximi.io, InBeacon.co, although other platforms are available too.
Install Beacons
Place a beacon in any place in the mapped building or room. Switch it on, so now beacon starts to send a signal.
Mark Beacons on the Map
Use specific software for marking each beacon’s location on the map. It means just point a dot on the map and write (x, y) coordinates (usually in meters relatively to zero-point).
Track an Object
Once a beacon is installed and turned on, it starts to advertise its identifier. Any smart device now can discover this ID, and identify the position of the beacon using its internal database of the mapped building. It is possible that a smart device can just transmit data to a server. Then the server estimates the device location relative to the BLE nodes known locations.
How Many Beacons should be?
For more precise positioning more beacons are required. The exact number depends not just on the size of the space, but also required accuracy, how the space is arranged (furniture, etc.), how crowded it gets, etc. This is very rough estimate for near 5 m accuracy:
1,000 m2 => 20 beacons
10,000 m2 => 150 beacons
Also, you can use online calculator that makes it possible to determine how many beacons should be installed in a building depending on factors such as area and type of an object.
Type of Beacons
Two main standards currently are Apple’s iBeacon and Google’s Eddystone. Also there are some alternatives like URIBeacon and ALTBeacon but it does not seem that these alternatives are particularly popular now.
iBeacon entered the market in 2013 and was the first in BLE tracking. It is now the leading standard for BLE proximity sensing. Eddystone is relatively young technology (announced in 2015), but it is gaining popularity very fast. At the end of 2016, 56% of Proximity.directory members are supporting Eddystone, which is x1.5 increase since the end of 2015.
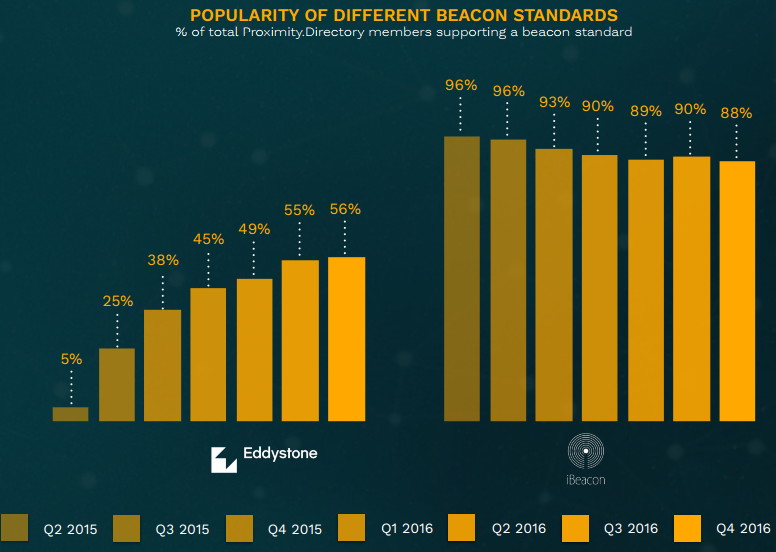
From a user’s point of view (energy consumption, proximity, strength of signal), there’s little difference between iBeacon and Eddystone standard. But differences are huge when you are developer. In general, iBeacon is simple, time proven and proprietary. Eddystone is secure, public, but a little more complex. The following table provides a comparative look at the details and differences.
| Apple’s iBeacon | Google’s Eddystone | |
|---|---|---|
| Compatibility | Android and iOS. But developed native only for iOS. | Cross-platform. Compatible with any platform that supports BLE beacons. |
| Profile | It is a proprietary software. Thus, the specification is controlled by Apple. | It is open-source. The specification is published openly on GitHub. |
| Ease of use | Simple to implement. | Since it sends more packets of information than iBeacon requires more complicated coding. |
| Broadcasted packets | iBeacon broadcasts only one advertising packet which has a unique ID number comprising of three parts – UUID, Major, and Minor. | Eddystone broadcasts three different packets: unique ID number, URL address, sensor telemetry. |
| Usage | The device would need a specific app to do a particular task. | Eddystone, on the other hand, sends out URL which can be opened in a web browser or specific apps. |
| Security and Privacy | There is no specific feature. The signal transmitted by a beacon is a public signal. | Eddystone has EID (Ephemeral ID) that changes in few minutes. Such signal can only be identified by “authorized clients”. |
| API | Apple has no specific API made available for iBeacon fleet management. | Google has launched two APIs (Nearby API and Proximity Beacon API) that make Eddystone beacons more powerful. |
BLE Beacon’s Vendors
Who are the producers of beacons? There are many popular proximity solution providers, some of the most known are: Kontakt.io (Poland), Estimote (UK), Cisco Meraki (US), Accent Systems (Spain), Sensoro (US), and others.
How Much Does a Beacon Cost?
A beacon may cost anywhere between $5 and $45, depending on the vendor, functional scope, and battery type.
BLE Restrictions
And finally it is important to keep in mind the limitations for a BLE tracking system.
Noise: Bluetooth LE protocol operates at 2.4 GHz frequency. And the same frequency is used by ISM, IEEE 802.11, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n Wireless LAN WIFI, IEEE 802.15.4-2006, ZigBee, among many other protocols and technologies. That is why the performance of a BLE tracking system can be disrupted by a noise from other wireless devices operating in the same spectrum. Fortunately, Bluetooth LE uses an adaptive frequency hopping spread-spectrum within an 83 MHz ISM band, which also increases its robustness against interfering radio signals in the range of 2.4–2.483 GHz.
Relatively low precision: Practically beacons can define the orientation of an object with 1-3 m accuracy. This is not enough for some implementations like determining the location of small spare parts in a warehouse. The solution is to use Ultra-Wideband technology which is capable of defining a location with a 10–30 cm accuracy.
Relatively small range: At best a beacon will broadcast its signal up to 30 m. But in real conditions this distance likely be much smaller because of walls and noise.
Fortunately, the new Bluetooth 5 specification improves possibilities for future BLE-modules. Range should increase up to four times, and broadcast messaging capacity to eight times.
Sources of images used in the article: tune.com, drakecooper.com, beacon+circuit+board+antenna+chip, www.vs.inf.ethz.ch.






